
You might have often wondered why is eating meat bad for the environment? We hardly ever think of the repercussions of eating a beautiful piece of rib-eye steak. A piece of red meat makes most of us forget the worries and woes of the day.
Yet, we can’t turn a blind eye to the ever-increasing carbon footprint of the meat industry. So, we are going to have a serious talk throughout the article and explain 7 reasons why is eating meat bad for the environment.
Why is Eating Meat Bad for the Environment?
Our diet plays a significant role in the well-being of the environment that we live in. Consequently, the ever-growing population of the Earth requires more food and resources.
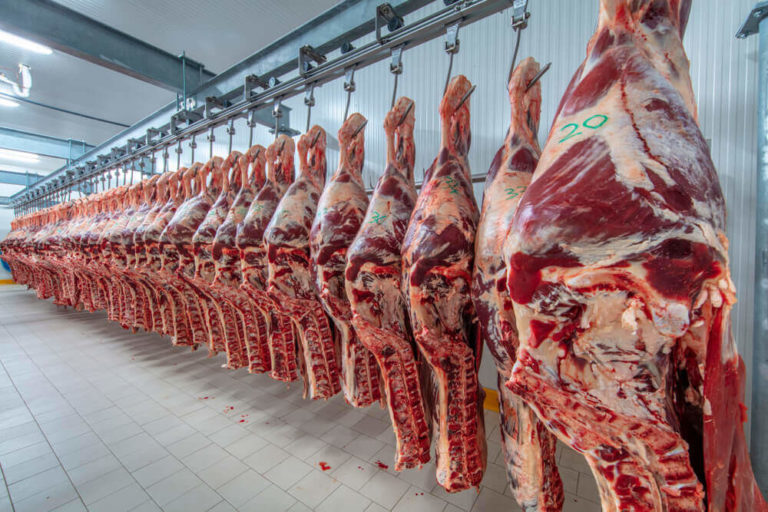

Subsequently, we can not ignore the nutritional value of meat. However, its toll on the environment is far too heavy. So, without further ado, let’s discuss 7 reasons why is eating meat bad for the environment.
1. Deforestation
When we discuss why is eating meat bad for the environment, it is hard to see how it adds up to deforestation. However, directly or indirectly, the production of meat is related to deforestation in South America.
In the Amazon rainforest, soy and beef production are responsible for deforestation, according to WWF. Consequently, deforestation is also happening in countries like Argentina and Paraguay.
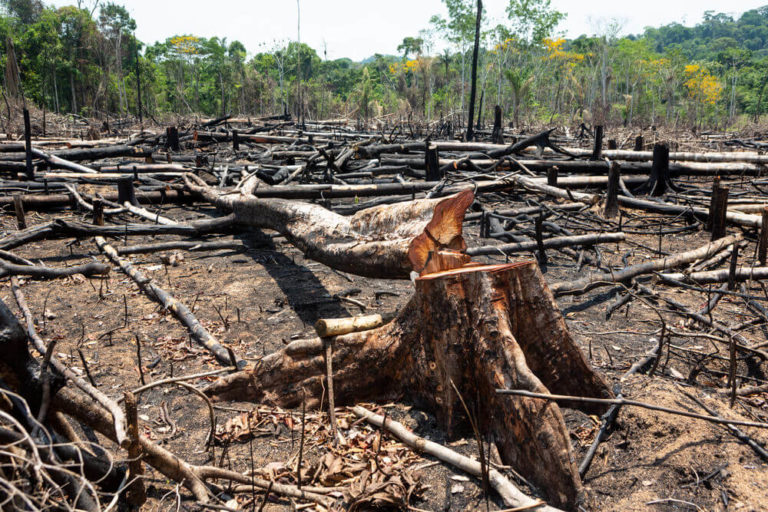

Farmers clear a vast amount of forest land to make space for cattle grazing. Moreover, farmers also clear the land for growing industrial animal feed. More often than not, they burn a fire to clear the lands. You might have seen in the news, frequent forest fires are threatening the existence of the Amazon rainforest in recent years.
The fires lead to a huge amount of carbon emissions. And deforestations remove a huge number of CO2 sinks.
2. Loss of Biodiversity
Why is eating meat bad for the environment, you ask? Biodiversity is the direct consequence of deforestation. And we know how deforestation is happening to farm industry animals. And to meet the huge demand for meat globally.

The meat industry directly contributes to the extinction of thousands of species. In addition, clearing forests destroys the habitats of wildlife. Destruction of the natural environment causes many species to extinct. Consequently, it disturbs the ecological balance. However, biodiversity is essential for food, natural water, and medicines.
Currently, almost half of the habitable land on Earth is used for farming. And meat industries use more than 77% of that share solely for the purpose of grazing cattle and producing animal feed. Thus, the loss of biodiversity is a threat to the existence of mankind as well.
3. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The release of greenhouse gases such as Methane, CO2, Nitrous Oxide causes climate change. In addition, an excessive increase in the consumption of meat is causing businesses and farmers to graze more cattle.
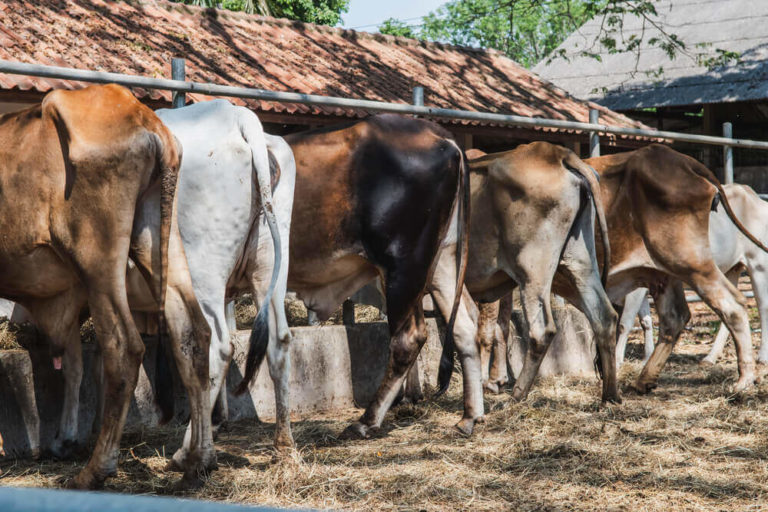

This in turn raises the level of greenhouse gas emission at an alarming rate. Greenhouse gas is the primary cause of global warming. So, next time someone asks why is meat bad for the environment, tell them about greenhouse gas emissions.
Livestock farming contributes to greenhouse gas emissions in several ways:
Destruction of the forests disturbs Ecosystem
The process of destroying the ecosystem causes a huge amount of CO2 emissions.
Raising Huge Amounts of Livestock
Animals create a large amount of methane gas in the process of digesting their food.
Use of Fertiliser
Soybean is the primary source of industrial animal feed. As a result, farmers use a huge amount of fertiliser during soybeans production. Unfortunately, these fertilisers are mostly nitrogen-based. And thus, it contributes to the emission of nitrous oxide.
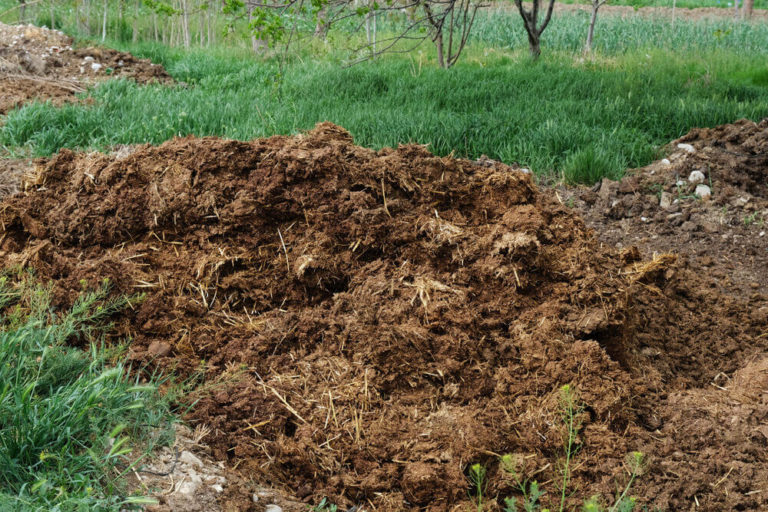

Decayed Manure
Animal manure produces a concentrated amount of methane gas, which gets mixed with the environment. Especially, cow manure contains one of the highest amounts of methane gas.
4. Water Usage
Meat production uses a lot of water. And beef is the most water-intensive food. Beef uses two times as much water as pork. And it uses four times as much as alternative protein sources like lentils. Producing a pound of meat requires 2500 gallons of water. In contrast, producing wheat only requires 25 gallons of water for a pound.
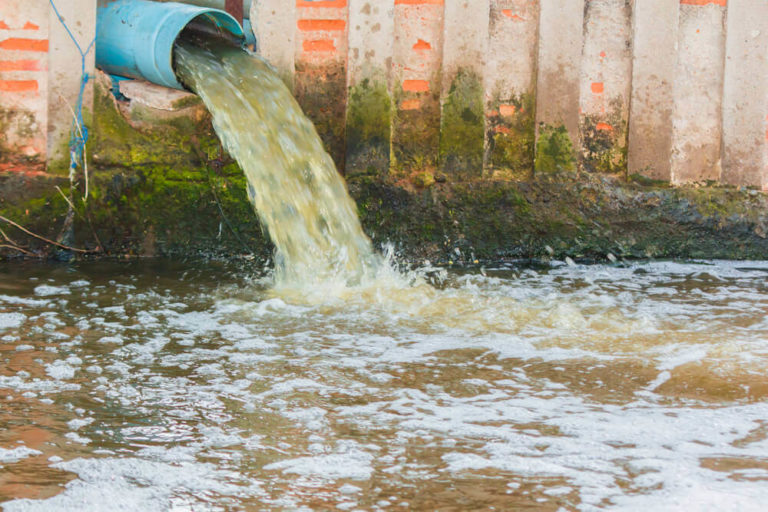

Consequently, it is not just cow meat that is the problem. According to People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals (PETA), the amount of waste that a pig factory produces equals the waste produced by a city of 12,000 people. Most times, the raw waste is thrown directly into the environment.
It is a fact that soybean growing (for animal feed) is inefficient in terms of water use. Thus, it further exacerbates the problem of water waste. In addition, livestock production also adds to global water pollution. It does so by contaminating watercourses with manure.
5. Increased Risk of Future Pandemics
Deforestation and other forms of wild land destruction happen mostly for animal agriculture. These are key contributors to the spread of novel infectious illnesses. Animals are responsible for three-quarters of new human diseases. Next time you ponder why is eating meat bad for the environment, think of Coronavirus.

Scientists insinuated noble Sars-Cov2 virus came from the species of bats or some other exotic animals. When people disturb or destroy the forest, they destroy the habitats of such species as well. And they tend to head for living in our local environment.
When forests are cut down and burned, wildlife comes into closer contact with humans. The close proximity puts us at great risk. Subsequently, it allows dangerous illnesses to spread from animals to humans. The higher the destruction of forest, the greater the likelihood of a new pandemic.
But industrial beef isn’t the main source of sickness. Factory farms are responsible for accelerating the disease transmission process between animals. And in turn, it transmits from animals to humans.
Subsequently, the risk is increased in industrial meat farms. Because animals have weaker immune systems. And we all know how numerous animals are squeezed into small spaces in these farms. This means that viruses can evolve faster and have a higher chance of infecting humans.
6. Less Meat Consumption can End World Hunger
10 to 11 billion people can be fed with the calories we produce on a global scale. However, industries channel the vast bulk of this food to farm animals rather than people in need.
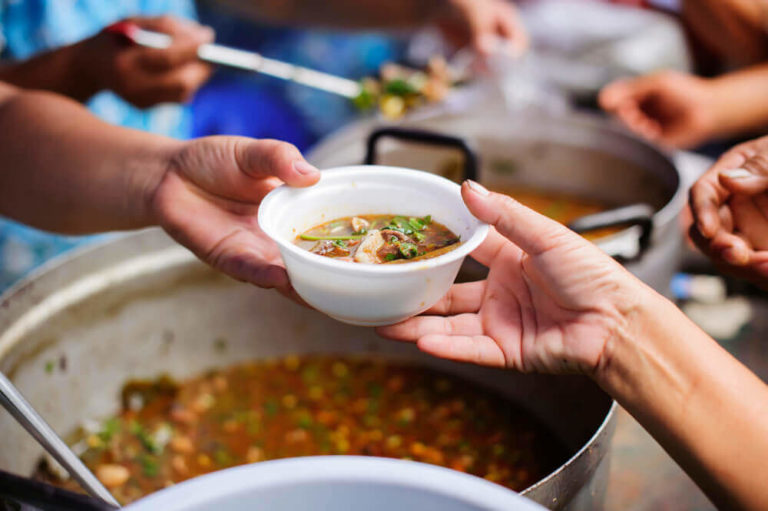

Subsequently, crops that people could eat are being used to fatten up animals for meat. And millions of people going hungry every day is a direct consequence of this. To make 1 pound of flesh, cows must ingest 16 pounds of grass or crops. In the USA, more than 80% of the harvested corn is fed to animals.
Animals consume around 2 tons of each 5 tons of grain produced worldwide, as per Worldwatch Institute. Thus, a decrease in consumption of meat may release vast grain quantities. And, it will further alleviate land pressure.
7. Human Rights Abuse & Land Theft
The Equality and Human Rights Commission did research on the UK meat sector. The research has shown that maltreatment of workers in factories is widespread. Particularly, migration workers are exploited in abattoirs and factories.
Consequently, owners discriminate against and bully migrant workers. Also, managerial abuse and insecure working conditions are common phenomena. Some workers had to work 90 hours a week.
Moreover, factory managers do not allow pregnant women to go to the toilet for lengthy hours. They are usually one of the poorest and most exploited workers in the country.

The indigenous peoples of Brazil are at the frontline in fighting to safeguard forests and traditional villages. Consequently, President Bolsonaro and his government are tacitly encouraging illegal loggers and farmers to occupy the indigenous lands. They are doing so by implementing historical legislation and legalizing land grabs.
In these battles, land invasions are often violent and loggers murdered the indigenous. Subsequently, JBS company is a producer of mass meat. It has regularly been associated with providers operating illegally in protected indigenous areas.
An investigation found serious implications of poor working conditions in JBS owned abattoirs. Also, the investigation found several reports of Covid-19 outbreaks and salmonella-infested chicken exports.
So, next time your friends invite you out for having a steak, think of the human cost of eating it. Explain to your friends why is eating meat bad for the environment.
Negative Impact on Health
We’ve covered the part about why is eating meat bad for the environment. Now, let’s come to the part where we discuss why meat is bad for your health. Several diseases are linked to diets high in red and processed meats. Diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer are some of these diseases.

A person living in a high-income country typically consumes 200-250gm of meat per day. However, the UN advises the meat consumption per person should be no more than 80-90 grams per day.
Consequently, high-fat dairy foods and processed foods lead to complex obesity. And a sugar-based diet can lead to significant organ failure. Subsequently, sugar can be addictive and ages your body quicker. In contrast, health experts link fibre-rich diets to a lower incidence of certain diseases. Diets enriched with fruits and vegetables are fibre rich diets.
By 2050, switching to a more plant-based diet could save up to 8 million lives each year. Consequently, it will result in $1.5 trillion in healthcare savings. And mitigation of climate change impacts will occur. Subsequently, a plant-based diet is much more accommodating to boost your immune system.
Enrol in the course Immunity Boosting Foods to learn about the strategies of boosting the immune system. The course will help you to understand the key details of cancer-fighting food and much more. Subsequently, this accredited course will be great to build up your CV if being a professional nutritionist interests you.
Alternatives to Eating Meat
We’ve discussed the reasons why is eating meat bad for the environment? Despite the environmental impact, meat is a rich source of protein. Meat may supply protein, amino acids, and numerous critical micronutrients.
These micronutrients are crucial for our diets, as we have already proved. So what are some alternatives to meat if we reduce meat consumption? There are a number of possibilities when we look into the advantages and disadvantages of alternating proteins.
Plant-based Protein
A high source of protein and other nutrients can be found from plant sources. Foods may include such as quinoa, soy, walnut, and amaranth.

Algae
We obtain an excellent source of protein and fatty acids from algae. Consequently, algae are a rich source of fibre as well. Also, vitamin B12 is abundant. It also produces more nutrients than other high-protein plants per unit area.
Insects
Insects that are edible provide a healthy source of protein and minerals. For instance, crickets are a good source of protein, iron, and vitamin B12. In addition, grasshopper, bee larvae and beetles are some other delectable bugs you can try.
Consequently, their commercial production has a considerably lower environmental impact. Greenhouse gas and water consumption of insects are way lower compared to meat. Moreover, accommodation of land is not necessary.
Cultured Meat
Cultured meat is the meat that has been cultivated in the labs. Food from the future could be generated by in vitro animal cell cultivation. It consumes less land and water.

Consequently, vitro cell meat minimizes pasture requirements. Moreover, food-borne infections are eliminated. Subsequently, the meat’s nutritional content can be higher. And fewer antimicrobials are needed.
However, these alternatives are fairly new in their field. So, it is understandable that not all risks are tested and minimized yet. Hence, there could be some potential downsides. Moreover, the socioeconomic cost and health implications still require a lot of research and study.
Final Words
According to Greenpeace, the UK population needs to cut back on meat and dairy by 70%. We have to do this to prevent a climate breakdown. This is a collective goal of the whole of the European Union to be achieved by 2030. Consequently, big supermarkets play a huge role in shaping customers demand. So, they need to play their part in achieving the goal.

Countries in Europe are already witnessing direct consequences of climate change. So, it is important for all of us to understand why is eating meat bad for the environment. It is high time we do our part to save our mother nature. And it is important that policymakers do a better job, too.
Find Your Ideal Course Today
Find Your Ideal Course Today
Recent Posts
- Tips for Making the Most of an Internship
- “Duvet Days” and 6 unusual perks for attracting talent
- How to Maximize Data Security in Virtual Data Rooms Effectively
- How Online Courses Can Help You Achieve Your Dream Career
- Crafting the Perfect CV for a Hospitality Management Job
- Is a Non-Clinical Career Right for You?
- 10 Ways to Improve Your Writing Skills
- Effective Communication in Nursing: The Key to Excellence
- 8 Qualities of a Good Teacher
- Is business development a good career?
 All Courses
All Courses Personal Development
Personal Development Business
Business Employability
Employability Management
Management Sports, Nutrition & Fitness
Sports, Nutrition & Fitness Microsoft Office
Microsoft Office Marketing
Marketing Health & Safety
Health & Safety Nursing & Care
Nursing & Care HR and Leadership
HR and Leadership Software
Software Counselling and Therapy
Counselling and Therapy Language
Language Accounting & Finance
Accounting & Finance QLS Endorsed
QLS Endorsed Teaching
Teaching Psychology
Psychology Teacher Training
Teacher Training Excel
Excel IT
IT Health and Care
Health and Care Lifestyle
Lifestyle Photography
Photography Physical & Mental Health
Physical & Mental Health Beauty
Beauty Powerpoint
Powerpoint Teaching & Education
Teaching & Education Animal Care
Animal Care Development
Development Bundle
Bundle Networking & Design
Networking & Design Health & Fitness
Health & Fitness Digital Marketing
Digital Marketing Teaching & Special Education
Teaching & Special Education Leadership & Management
Leadership & Management







7 responses on "7 Reasons Why Meat is Bad for The Environment"